Detecting Disease Pre-Cursors Before Disease Manifestation
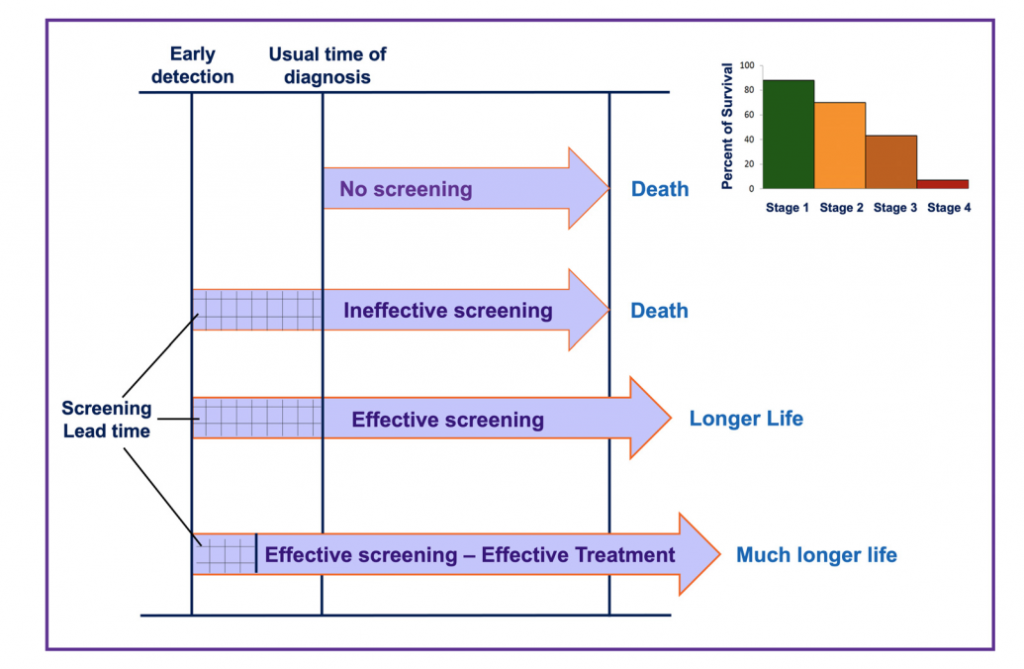
Effective screening for disease combines with effective treatment is the formula for much longer life.
Figure right: Schematic illustration of disease progression.
Some diseases are evidenced by “visual” observation of the inflammatory process, and one can readily follow the progression of the disease. Other inflammatory processors occur in internal organs; therefore, they are invisible, and the progression of the disease can be a “silent” event if not detected on time by invasive procedures such as colonoscopy for diagnosis of colorectal cancer. However, both inflammatory processes can be measured by the quantification of unique biomarkers in biological samples, which can categorize the stage of progression of the disease.
The area of the figure depicting the peaks labeled with letters A and B represents the quantity of an unmodified vs modified biomarkers, respectively, as the disease progresses.
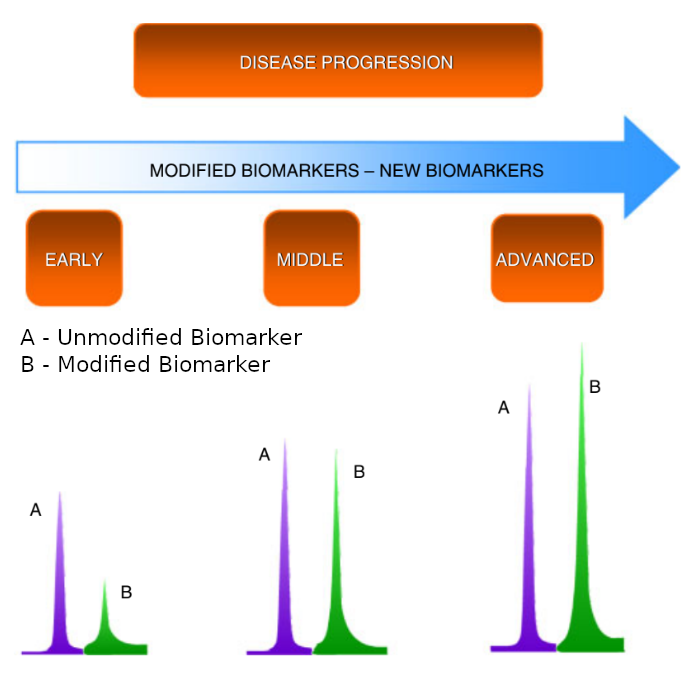
The key is Detecting Biomarkers of Early Stage Disease or Precursors in the Early Stages of Progression
Prostate Cancer Screening (PSA) Debacle
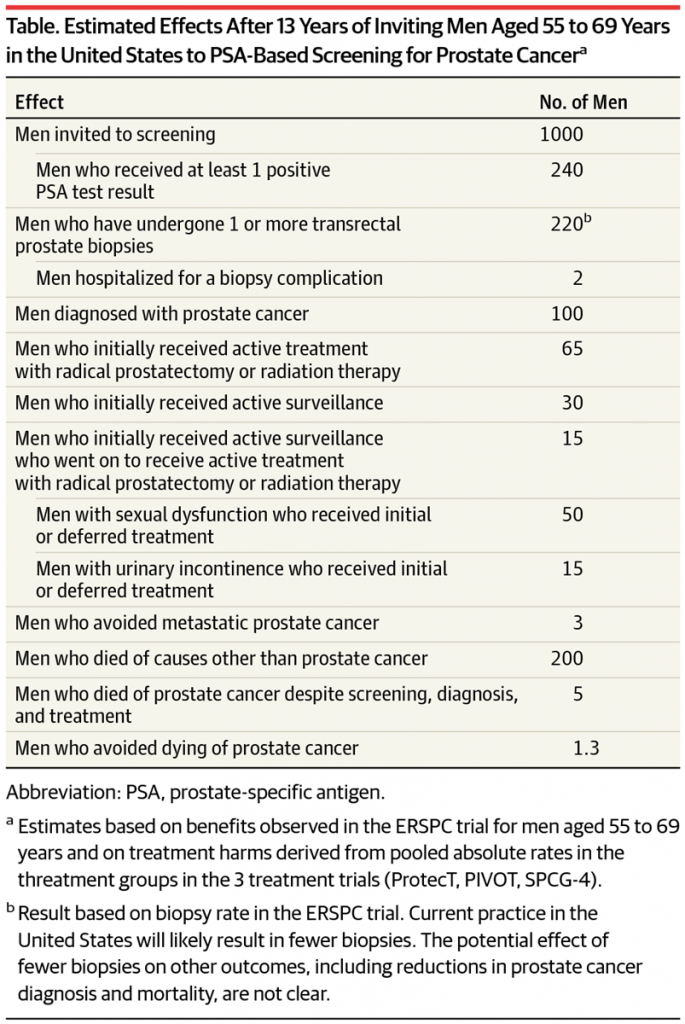
The above schematic demonstrates that for every 1000 men screened for prostate cancer, only one will avoid death from prostate cancer and three will avoid metastatic spread of the cancer, with the remaining men suffering psychological harm of a potential diagnosis of cancer, risks of prostate biopsy, and side effects of erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence from treatment of prostate cancer. While there is no clear evidence to recommend for or against prostate cancer screening, it is clear that potential harm from screening may outweigh the potential benefit for many individuals due to false positives, and lack of understanding of the severity of different prostate cancers.
Ultimately, a stronger emphasis and investment in prevention of disease through accurate screening tests would be much more practical and beneficial than waiting for the diseases to manifest themselves.
The clinical structure primarily functions on disease presentation where most of the health care spending is focused on treating rather than preventing chronic disease
Sources:
Guzman, biomolecules, 2021, 11(10), 1443
https://www.cdc.gov/chronicdisease/about/costs/
https://fightchronicdisease.org/sites/default/files/docs/PFCD_ChronDisease_FactSheet3Final.pdf
Based on the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, the united states spends approximately 75% of annual healthcare spending on treating chronic disease alone.
Sources:
Guzman, biomolecules, 2021, 11(10), 1443
https://www.cdc.gov/chronicdisease/about/costs/
https://fightchronicdisease.org/sites/default/files/docs/PFCD_ChronDisease_FactSheet3Final.pdf
Many chronic diseases are silent and may take several years to manifest their symptoms.
Sources:
Guzman, biomolecules, 2021, 11(10), 1443
Vago, R.,Trevisani, F. Circulating RNA in kidney cancer: What we know, and what we still suppose. Genes 2021,12, 835.
Ozgur, Y. Relationship between vitamin D deficiency, albuminuria, peripheral artery disease and 5-year mortality in chronic kidney disease. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2021, 30, 644-650
Carmichael F.; Fadavi, H.; Ishibashi, F.; Shore A.C.; Tavakoli, M. Advances in screening, early diagnosis, and accurate staging of diabetic neuropathy. Front. Endocrinal 2021, 12, 67 1267. [CrossRef]
Shaw, G. The silent disease. Nature 2016, 537,588-599. [Cross Ref] [PubMed]
Hanmer, J.; Yu, L.;Li,J.; Kavalierotos, D.; Peterson, L.; Hess, R. The diagnosis of asymptomatic disease is associated with fewer healthy days: A cross sectional analysis from the nationat heatth and nutrition examination survey. Br. J. Health Psychol. 2019, 24, 88-101. [CrossRef I Ptrblrtcd]
Saquib, N’; Saquib, I’; Ioaruridis,
meta-analyze
r.P.A’ Does screening for disease save lives in asymptomatic adults? systemic review of and randomized trials. Irr. l. Epiilemiot. ims,44,z*zn. iF-b’M;i Cebey-L6pez, M’; Salat A. Recognizing the asymptomatic enem y. Lancctirtyea. ois-. 2o2t,2l,5Os-sOO. lCrossReft King P’; Peacock
In 1999, a large prospective study on type 2 diabetes mellitus published in the United Kingdom demonstrated that pancreatic beta cell dysfunction starts almost 10 years before patients are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Sources:
Guzman, biomolecules, 2021, 11(10), 1443
King P.; Peacock, l.; Donnelly, R. The UK Prospective Diabetes study (UKPDS): clinical and therapeutic impticarions for type 2 diabetes. Br. J. CIin. Pharnacol. 1999,48,643-648. [CrossRef]
Russo, G.T.; Giorda, C.B.; Cercone, S.; Nicolucci, A.; Cucinotta, D.; on behalf of BetaDecline Group. Factors associaled with beta-cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: The BetaDecline study,. pLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109702
The consequence of this based on current testing is that patients will have already lost up to 50% of their beta cell function by the time practitioners are able to diagnose them with this disease, making treatment and cure of the disease much more difficult.
Russo, G.T.; Giorda, C.B.; Cercone, S.; Nicolucci, A.; Cucinotta, D.; on behalf of BetaDecline Group. Factors associaled with beta-cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: The BetaDecline study,. pLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109702. [CrossRef]
Kahn, S.E. Clinical review 135: The importance of beta-cell failure in the development and progession of type 2 diabetes. J. clin. Endocr. Metabol. 2001, 86, 4047-4048 [CrossRef]
White, M.G.; Shaw, J.A.M.; Taylor, R. Type 2 diabetes: The pathologic basis of reversible B-cell dysfuncrion. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 2080-2088. [CrossRef]
Holman, R.R. Assessing the potential for alpha-glucosidase inhibitors in prediabetic states. Diab. Res. clin. pract. 1998,40 (suppl. S1), S21-S25
In a study of the evolutionary history of 2658 cancers, researchers determined that there are genetic mutations that occur far before the clinical manifestation of cancers that can be detected
For example, in the case of nucleic acid mutations, the rate of cytosine guanine to thymine guanine mutations can be a surrogate to predict latency of presentation of disease. With ovarian adenocarcinoma presenting up to 30 years after the occurrence of these mutations.
Sources:.
Gerstung, M.; Jolly, C.; Leshchiner, I.; Dentro, S.C.; Gonzalez, S.; Rosebrock, D.; Mitchell, T.J.; Rubanova, Y.; Anur, P.; Yu, K.; et al. The evolutionary history of 2,658 cancers. Nature 2020, 578, 122-128 [Crossref]
Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1443 p.2
Prostate Cancer Screening (PSA) Debacle

The above schematic demonstrates that for every 1000 men screened for prostate cancer, only one will avoid death from prostate cancer and three will avoid metastatic spread of the cancer, with the remaining men suffering psychological harm of a potential diagnosis of cancer, risks of prostate biopsy, and side effects of erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence from treatment of prostate cancer. While there is no clear evidence to recommend for or against prostate cancer screening, it is clear that potential harm from screening may outweigh the potential benefit for many individuals due to false positives, and lack of understanding of the severity of different prostate cancers.
Ultimately, a stronger emphasis and investment in prevention of disease through accurate screening tests would be much more practical and beneficial than waiting for the diseases to manifest themselves.
IN SUMMARY, Current biomarker detection methods either not accurate enough, or not cost-effective or practical for Point of Care TestingTHERE IS A SERIOUS SHORTCOMING IN THE QUALITY, SENSITIVITY, SELECTIVITY, AND SPECIFICITY OF CURRENT METHODS OF DETECING BIOMARKER PRECURSORS OF DISEASE.
The majority of laboratory diagnostic testing is now carried out via immunoassays, which have proved reliable after clinical suspicion for disease is moderate to high. Nevertheless, current immunoassays remain limited when applied to early detection of disease due to Poly reactivity of their antibodies the presence of interfering substance in the sample, and concentrations of biomarkers below levels of detection. Current immunoassay technologies are :
ELISA (Enzyme Linked ImmunoAssay) for detailed laboratory testing
LFTA for cost effective cartridge based POCT (Point Of Care Testing)

Dr. Norberto Guzman
Principle Scientist
ELISA
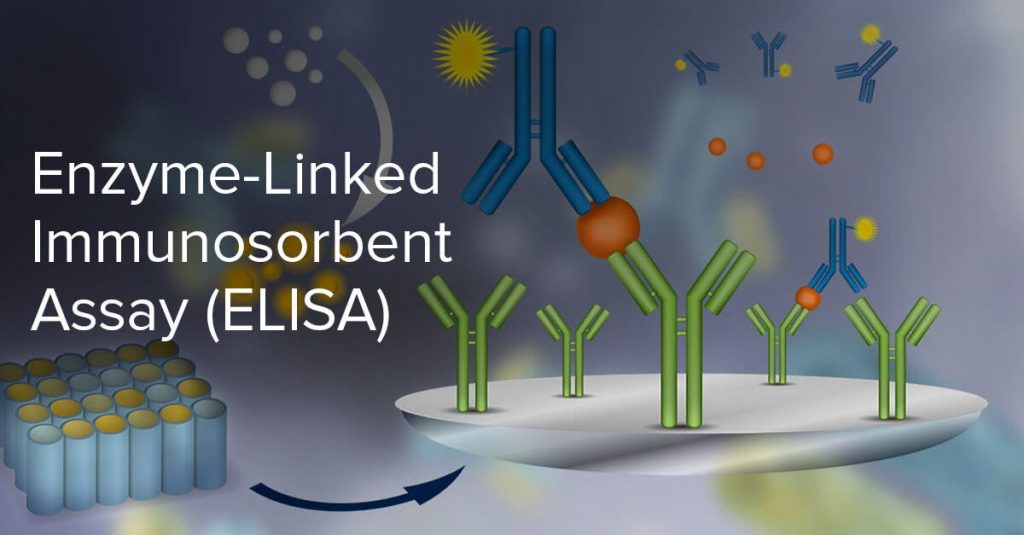
As a brief summary, ELISA technology detects biomarkers in biosamples by binding the target biomarker with an antigen specific for the biomarker compound. The term immunosorbent refers to the antigen-antibody binding reaction. Certain enzymes can then be used to link to the binding substrate that in turn causes a color change indicating detection.
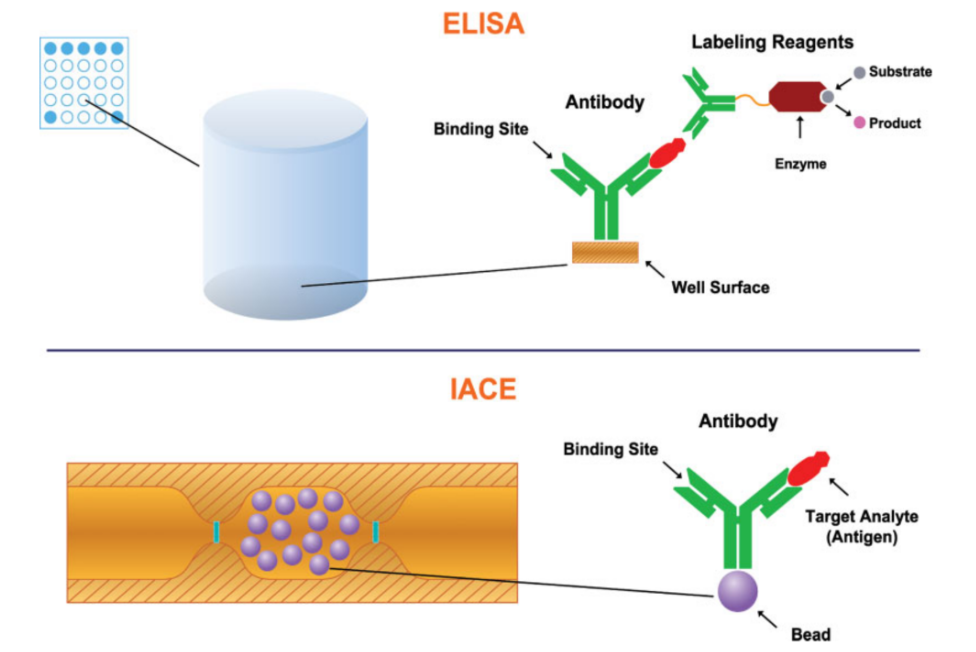
ELISA Advantages:
- Traditional, Most Commonly Used Immuno-Capture technique
- Convenient and Cost Effective Plate Well Based Assay Technique
- Has played central role in diagnosis and clinical research application
- Measurable signal allowing quantitative analysis
- Highly Sensitive, low concentrations of analytes measurable
- High Specificity; accurately differentiates analytes
- Broad Applicability: proteins, peptides, antibodies, hormones
- Automation allows for higher throughput
- Easy to Perform: sophisticated equipment, specialized training not required
Disadvantages:
- Mono dimensional technique
- Single use plate well
- Equipment cost
- Plate well incubation and analysis time
- Polyreactive antibodies often yield false positive biomarkers
- Not accurate enough in some isoform cases
